Lab-Grown Diamonds

Lab-grown diamonds have emerged as a response to the environmental and ethical concerns associated with natural diamonds. Offering greater transparency and high-quality stones at more affordable prices, lab-grown diamonds have become a growing trend. However, some people may have lingering misconceptions or uncertainties since the concept is still relatively new. As such, we're here to clear things up and help you feel confident and informed when deciding on lab-grown diamonds.
What Are Lab-Grown Diamonds?
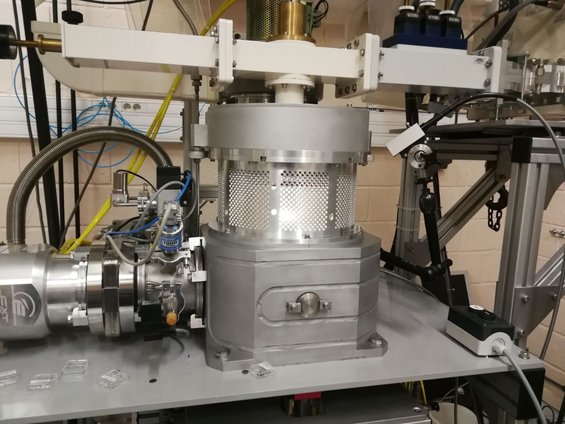
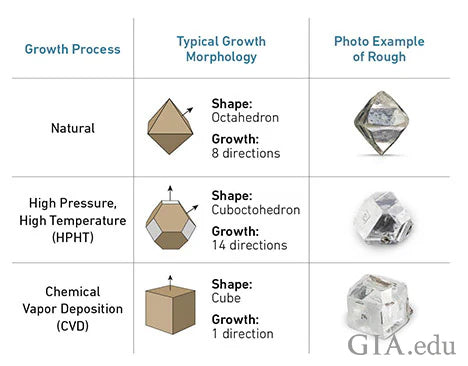
As the name suggests, lab-grown diamonds are created in laboratories using advanced technology that replicates the natural diamond-growing process. This allows lab diamonds to be chemically, physically, and visually identical to mined diamonds. Both types are made from pure carbon, formed under high pressure and high temperature. The only real difference is the origin of that environment—either deep within the Earth or inside a lab.
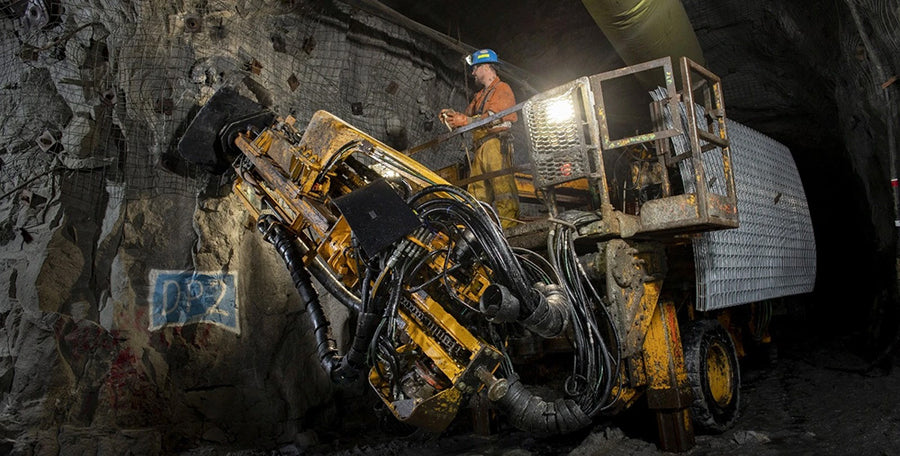
Currently, there are several different methods available for creating lab-grown diamonds, such as High Pressure-High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While both methods create beautiful, sparkling diamonds that are identical to natural diamonds and pass a diamond tester, there are some critical differences between them.
High Pressure-High Temperature (HPHT)
Lab diamonds created using the HPHT method undergo high pressure and high temperatures to transform carbon into diamonds, fully mimicking the creation process of mined diamonds. This process gives lab-grown diamonds a more natural look and can have inclusions similar to mined diamonds. However, this process requires more complex and expensive equipment than the CVD method.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Lab diamonds created using the CVD method are created by layering carbon atoms onto a diamond seed in a vacuum chamber. This allows for more direct control over the diamond's growth and characteristics, producing diamonds with higher clarity and color more consistently. Diamonds grown using this method lack nitrogen and/or boron impurities due to never being exposed to nitrogen at any point in the process.
Why Choose Lab-Grown Diamonds?
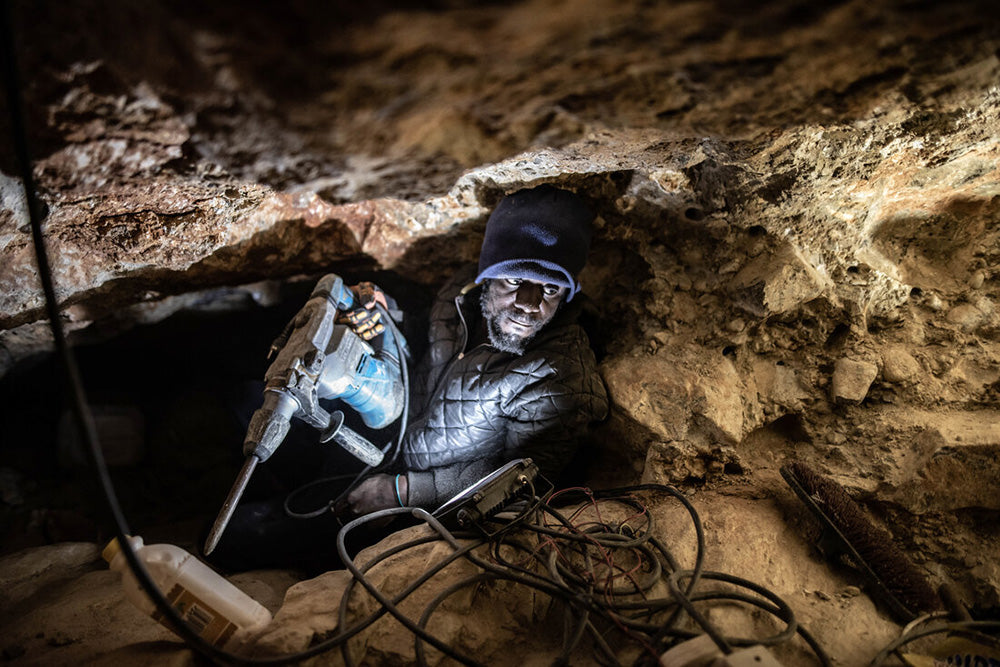
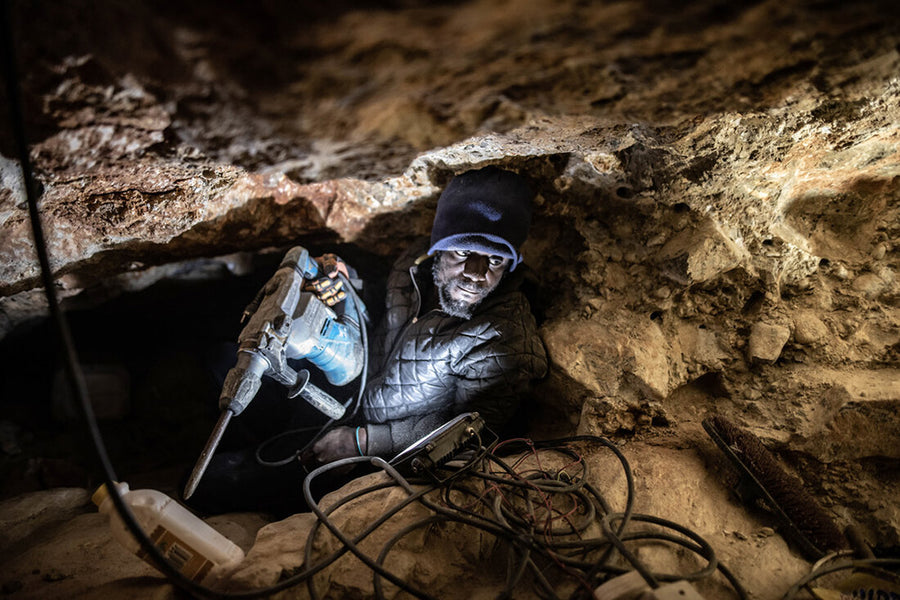
Mined diamonds come from a questionable and unethical supply chain. Diamond miners endure harsh working conditions, receive low wages, and face numerous human rights violations. At the same time, the mining sites themselves cause soil erosion, deforestation, and the destruction of entire ecosystems. This is why many people refer to mined diamonds as 'Blood Diamonds.' They are neither suitable for the people involved nor the planet.
Fun Fact: You must dig through about 88,000 to 176,000 pounds of Earth to find a single diamond!
On the other hand, lab-grown diamonds offer an ethical and environmentally friendly alternative that you can feel good about. They are ethically and environmentally friendly because they replicate the creation process in a controlled environment. While there is still room for improvement, lab-grown diamonds represent a significant step forward in the right direction. We are at the beginning of a 'Diamond Revolution.'
Lab-Grown Diamonds
- Complete control over the process
- Transparent supply chains
- Fair wages and good working conditions
Mined Diamonds
- Unethical supply chains from conflict regions
- Poor working conditions, low wages, and human rights violations
Lab-Grown Diamonds
- Reduced levels of energy required
- Less harmful to the environment and the surrounding communities
Mined Diamonds
- Causes soil erosion, displaced Earth, deforestation, and the destruction of ecosystems
Lab-Grown Diamonds
- Chemically, physically, and visually identical to mined diamonds
- Graded using the standard 4Cs of diamond quality
Mined Diamonds
- The same quality and grading, yet with a negative impact left behind
Lab-Grown Diamonds
- More affordable
- Better quality diamonds for similar or less than their mined counterparts
Mined Diamonds
- Have 'rarity' due to difficulties in mining, causing only 30% of mined diamonds to match the standards for diamond quality
A Closer Look At The Ethical & Environmental Impact
While we briefly touched upon the environmental impacts of diamond mining, the full extent of its impact on our planet goes much further than that. Within the mining regions, entire ecosystems and communities are disrupted and severely impacted.
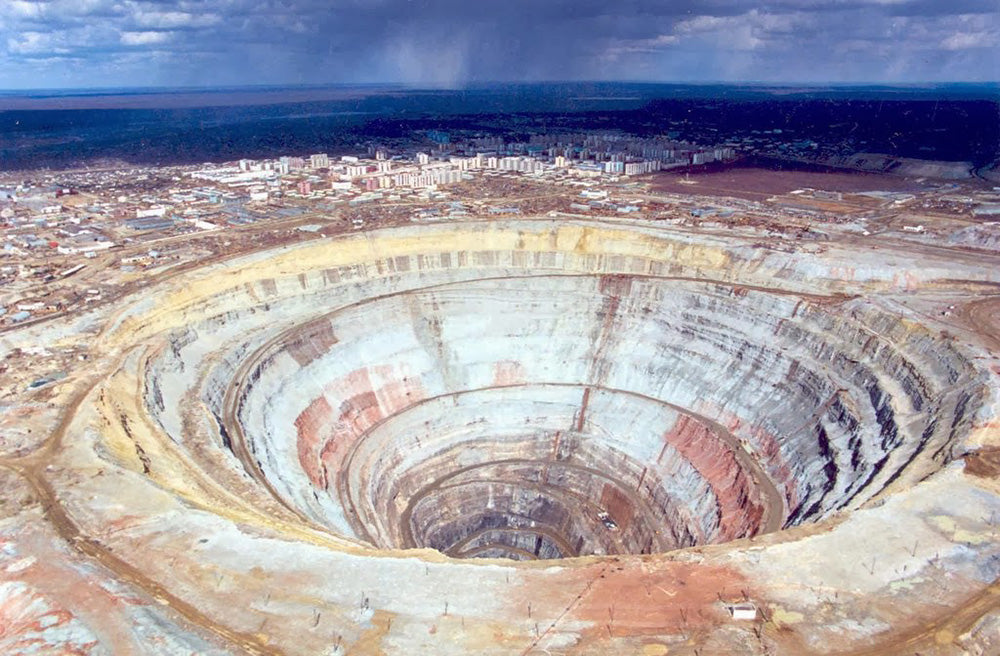
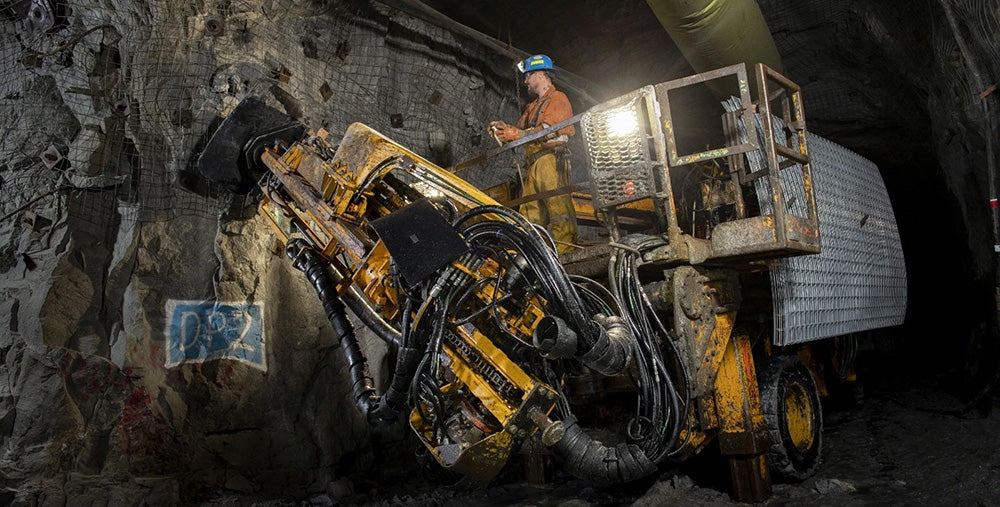
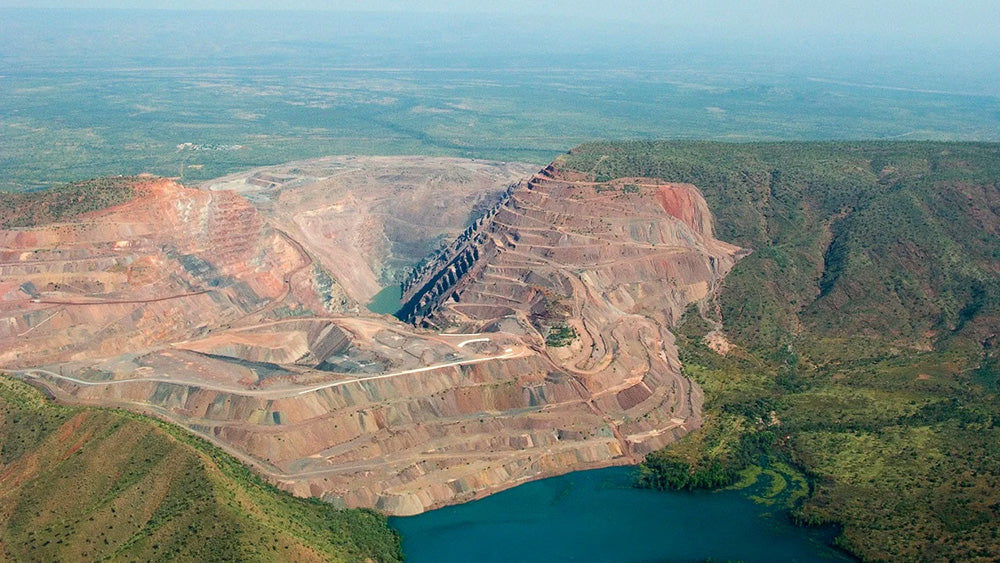
Kimberlite pipes, igneous rock formed from cooled molten magma, transport diamonds from the Earth's mantle to the surface. Two types of mines are used to access these pipes: open-pit and underground. Open-pit diamond mines maintain exposure to the Earth's surface throughout extraction, while underground diamond mines utilize horizontal and/or vertical tunnels for access.
Both methods require tons of debris to be removed using heavy machinery and explosives, which permanently disfigures the Earth. Additionally, when sediment and erosion from kimberlite pipes cause diamonds to accumulate, entire lakes may be drained, and rivers can be rerouted.
Mining diamonds, regardless of the method used, has led to the destruction of entire ecosystems.
Take Kono, Sierra Leone, for example. The abandoned mining pits have long since forced out the natural wildlife that used to call this area home. And it’s not just the animals that suffer—farming has become impossible because the topsoil has eroded, and the abandoned mines fill with unsanitary rainwater, creating a breeding ground for disease-carrying mosquitoes.
Another example of the terrible effects of diamond mining is the Paiter-Suruí tribe in the Amazon rainforest. When outsiders discovered that their land sat on 248,000 hectares of diamond reserves, the tribe was displaced, and the beautiful forest was left with irreversible damage.
As shown briefly, communities near mining pits are often forced to relocate. The unhealthy living environments and loss of their traditional ways of life, especially in rural areas, leave them with little choice.
For instance, in 2011, the people of Chiadzwa in Marange faced this harsh reality. After diamond miners moved into the area, they were displaced and relocated. While some measures were taken initially to prevent homelessness, ongoing support and compensation was uncertain. As such, the villagers lacked the resources to rebuild their lives and community. Instead of fostering self-sufficiency like intended, the limited compensation led to a dependency on the future aid that never came.
Mined diamonds generate around 140 pounds of carbon dioxide per carat. In 2023 alone, the 111.5 million carats produced resulted in approximately 15.61 billion pounds of carbon emissions—about the same as 1.5 million cars on the road for a year.
How To Differentiate Between Them?
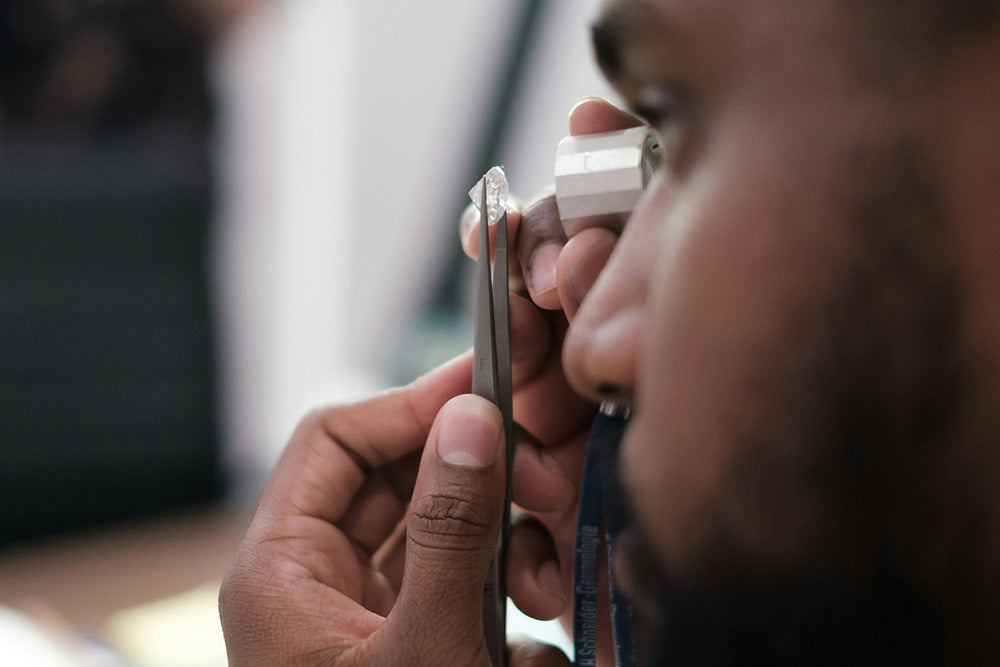
It can be challenging to tell mined and lab-grown diamonds apart. Even expert gemologists can't spot the difference just by looking; in fact, there have been numerous cases of mix-ups because visually, they're identical. The only way to distinguish them is by using a specialized machine that analyzes the atomic structure. For this reason, major diamond grading institutes like GIA, HRD, and IGI now use the same standards to grade both lab-grown and mined diamonds.
The FTC also recently updated its definition of a diamond, removing the word "natural," as the only difference between lab-grown and mined diamonds is their origin. Without considering the origin, both types are exactly the same.
Lab-Grown Diamonds VS Cubic Zirconia
Cubic Zirconia are fake diamonds. While some can look convincing, they do not contain carbon and are softer than real diamonds.
As Stephan Morisseau, a spokesperson for the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), puts it, "[Lab-created diamonds] are not fakes. They're not cubic zirconias. They have all the same physical and chemical properties of a mined diamond."
How To Buy Lab-Grown Diamonds?
Buying diamonds can feel overwhelming if you're unsure where to start. With so many options available, knowing who to trust and what to look for is tough. To help, we've gathered the essential knowledge you need to confidently find the perfect diamond for you and your dream piece.
Research the brand you’re considering. Some claim to be reputable and ethical but offer little proof to support those claims. Schedule a consultation with an expert to ensure you know exactly who you’re sourcing your diamonds from and can trust their practices.
Choosing a diamond shape is a great starting point when shopping for the perfect diamond. Are you drawn to a classic round, emerald, or pear cut? Or do you want something unique, like a heart, asscher, or marquise cut? Each diamond cut requires precise artistry to achieve the correct proportions, symmetry, and polish to ensure the diamond sparkles at its full potential.
How big of a diamond are you looking for? Carats are the units used to measure a diamond's weight, with one carat being equivalent to 200 milligrams. All else being equal, diamonds increase in price with each step up in carat weight.
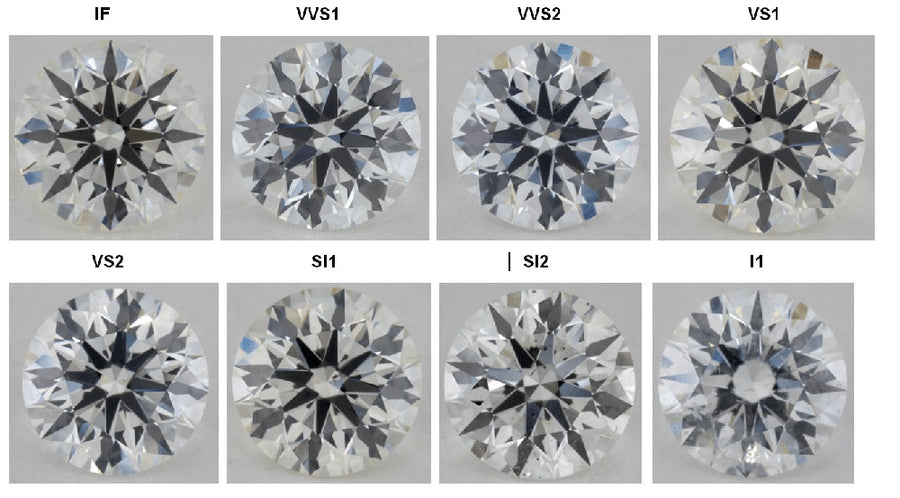
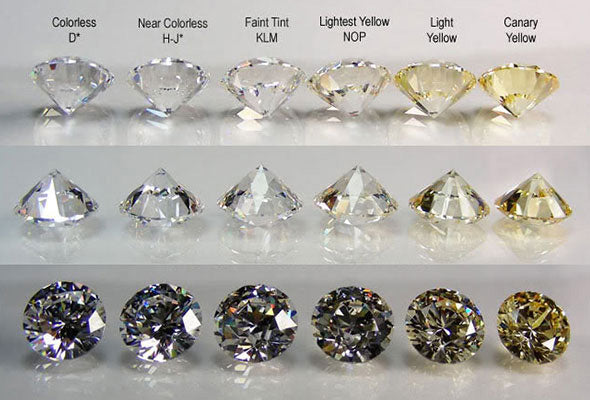
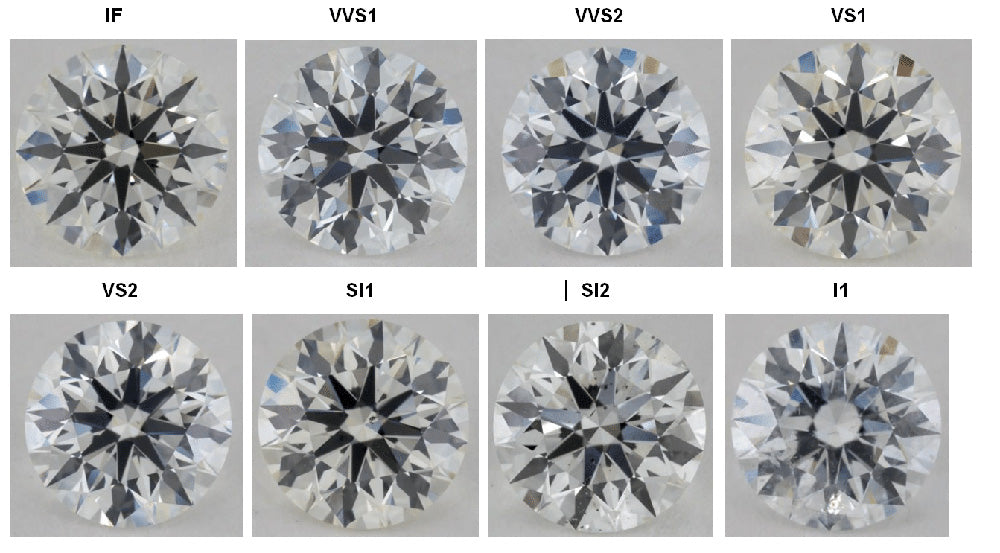
Diamonds are primarily valued for two fundamental properties: clarity and color. Clarity refers to a diamond's purity, ranging from near-flawless under magnification to having visible internal inclusions and/or external blemishes. Color, on the other hand, is graded by the absence of color, with the highest quality rated as "D" and the lowest as "Z." Chemically pure and structurally perfect diamonds are colorless, possessing no hue at all.
Where Can You Buy Lab-Grown Diamonds?
Right here at Lovere!
For over six decades, Lovere has been committed to exceptional craftsmanship in our collection of lab-grown diamonds. Each piece is meticulously handcrafted by skilled artisans who blend traditional techniques with modern innovation. Every diamond tells a unique story, and our curated selection is handpicked for its beauty and ethical sourcing. From sparkling solitaire engagement rings to intricately elegant necklaces, each piece captures the essence of emotions and milestones. Rooted in tradition yet driven by innovation, we invite you to explore our exquisite collection and immerse yourself in the allure of ethical diamonds.